Research on the correlation between otorhinolaryngologic diseases and environmental meteorological factors in children
-
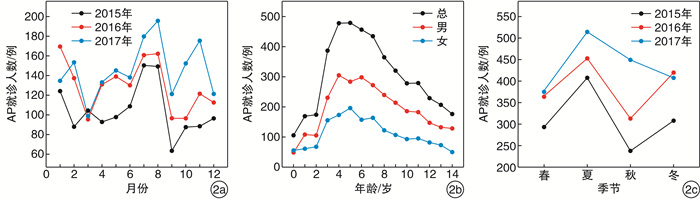
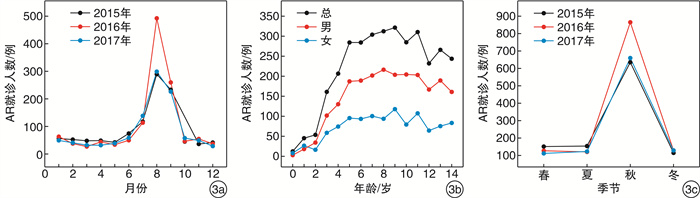
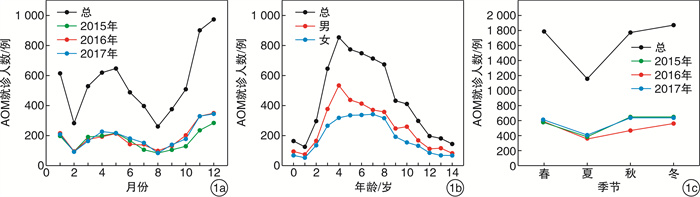
摘要: 目的 探讨兰州地区儿童急性中耳炎(AOM)、急性咽喉炎(AP)、变应性鼻炎(AR)与环境气象因素的相关性。方法 收集20l5—2017年期间解放军第940医院AOM、AP、AR患儿的临床资料,结合同期兰州市空气质量指数(AQI)及环境气象数据(PM2.5、PM10、CO、NO2、SO2、O3、平均气温、平均气压、平均风速、平均湿度),分析环境气象因素与儿童AOM、AP、AR就诊人数的相关性。结果 儿童AOM日就诊人数与AQI、PM2.5、PM10、CO、NO2、SO2、平均气压均呈正相关,与O3、平均气温、平均风速均呈负相关,而与平均湿度无相关性;儿童AP日就诊人数与平均温度、平均湿度呈正相关,与其他9项因子无相关性;儿童AR日就诊人数除与O3无相关性外,与其他10项因子存在相关。不同季节对儿童AOM、AP、AR日就诊人数的影响因素不同,环境气象因素对儿童AOM、AP、AR的发病具有单滞后和累积滞后效应,但单滞后和累积滞后时间具有一定的差异。结论 环境气象因素对儿童AOM、AP、AR的发病可能存在一定的相关性,且有滞后性,儿童AOM、AP、AR发病受季节因素的影响。Abstract: Objective To explore the correlation between acute otitis media(AOM), acute pharyngitis(AP) and allergic rhinitis(AR) and environmental-meteorological factors in children in Lanzhou.Method Data were collected in 2015-2017 from the outpatient department and emergency department of Otolaryngology of one hospital in Lanzhou. The association between clinical data and the environmental meteorological factors during the same period, including the air quality index(AQI), PM2.5, PM10, CO, NO2, SO2, O3, average temperature, average air pressure, average wind speed, average humidity in Lanzhou, was analyzed.Result The incidence of AOM was positively correlated with AQI, PM2.5, PM10, CO, NO2, SO2, average air pressure, and was negatively correlated with O3, average wind speed and average air temperature, but not correlated with average humidity. The incidence of AP was positively correlated with average temperature and average humidity, and not correlated with other 9 factors. The incidence of AR was correlated with all 10 environmental meteorological factors except for O3.The number of children with AOM, AP and AR varied with different seasons. Environmental meteorological factors have single lag and cumulative lag effects on the incidence of children with AOM, AP and AR, and difference between the single lag and cumulative lag time was observed.Conclusion There may be some correlation between the environmental meteorological factors and the incidence of AOM, AP, AR in children, and there is a lag effect. The incidence of pediatric AOM, AP and AR is affected by seasonal factors.
-
Key words:
- otitis media /
- pharyngitis /
- rhinitis, allergic /
- environmental meteorological factors /
- children
-

-
表 1 AOM、AP、AR日就诊人数与大气环境因素的相关性
环境因素 AOM AP AR AQI 0.1932) -0.005 -0.2212) PM2.5 0.2162) 0.017 -0.2082) PM10 0.1982) -0.025 -0.2392) SO2 0.1322) 0.025 -0.1102) CO 0.1842) 0.014 -0.1472) NO2 0.2062) -0.020 -0.1432) O3 -0.1392) -0.029 -0.002 平均温度 -0.2852) 0.0691) 0.3972) 平均气压 0.1352) -0.059 -0.0962) 平均湿度 -0.005 0.0601) 0.1292) 平均风速 -0.0641) -0.012 0.0731) 1)P < 0.05; 2)P < 0.01。 表 2 春季AOM、AP、AR日就诊人数与大气环境因素的相关性
环境因素 AOM AP AR AQI -0.038 -0.091 -0.031 PM2.5 -0.009 -0.1261) -0.063 PM10 -0.043 -0.1191) -0.038 CO -0.024 -0.019 -0.029 NO2 0.040 -0.026 -0.008 SO2 -0.047 -0.063 -0.012 O3 0.022 0.047 0.011 平均温度 0.1792) 0.086 0.079 平均气压 -0.047 -0.049 -0.065 平均湿度 0.018 0.086 -0.030 平均风速 -0.1211) 0.045 0.072 表 3 夏季AOM、AP、AR日就诊人数与大气环境因素的相关性
环境因素 AOM AP AR AQI 0.029 0.034 -0.1521) PM2.5 0.092 0.045 0.1511) PM10 -0.012 0.030 0.097 CO -0.047 0.101 0.1441) NO2 0.022 0.021 -0.076 SO2 0.091 0.030 -0.054 O3 -0.077 -0.039 0.027 平均温度 -0.1591) 0.057 0.1791) 平均气压 -0.093 -0.023 0.1391) 平均湿度 0.014 0.079 0.034 平均风速 0.026 0.004 -0.009 表 4 秋季AOM、AP、AR日就诊人数与大气环境因素的相关性
环境因素 AOM AP AR AQI 0.3212) 0.1461) -0.1852) PM2.5 0.3612) 0.2112) -0.2412) PM10 0.3032) 0.1421) -0.2132) CO 0.3352) 0.1742) -0.2172) NO2 0.2492) 0.004 -0.1672) SO2 0.2122) 0.1792) -0.1852) O3 -0.096 -0.1662) 0.1251) 平均温度 -0.5532) -0.1872) 0.5132) 平均气压 0.062 0.052 -0.1201) 平均湿度 -0.089 0.014 -0.017 平均风速 -0.100 -0.1271) 0.1361) 表 5 冬季AOM、AP、AR日就诊人数与大气环境因素的相关性
环境因素 AOM AP AR AQI 0.1231) -0.017 0.009 PM2.5 0.1852) 0.040 0.056 PM10 0.1622) -0.009 -0.024 CO 0.2382) 0.012 0.071 NO2 0.3112) 0.041 0.055 SO2 0.1291) 0.047 0.1221) O3 -0.3132) -0.035 0.066 平均温度 -0.1391) -0.098 -0.1291) 平均气压 0.2562) 0.021 -0.043 平均湿度 0.112 0.105 0.021 平均风速 -0.2152) -0.080 -0.044 表 6 环境气象因素对儿童耳鼻喉科相关疾病的单滞后效应分析
环境因素 疾病 单滞后1 d 单滞后2 d 单滞后3 d 单滞后4 d 单滞后5 d 单滞后6 d AQI AOM 0.1941) 0.1882) 0.2502) 0.2362) 0.2312) 0.2302) AP -0.014 -0.042 -0.005 -0.047 -0.043 -0.014 AR -0.2212) -0.2442) -0.2041) -0.2002) -0.2272) -0.2312) PM2.5 AOM 0.2152) 0.1962) 0.2502) 0.2462) 0.2432) 0.2362) AP 0.020 0.015 0.013 -0.034 -0.026 -0.003 AR -0.2112) -0.2422) -0.2072) -0.1972) -0.2012) -0.2172) PM10 AOM 0.2172) 0.1892) 0.2602) 0.2242) 0.2302) 0.2322) AP -0.039 -0.0601) -0.048 -0.0621) -0.0812) -0.049 AR -0.2392) -0.2472) -0.2162) -0.2242) -0.2612) -0.2632) SO2 AOM 0.1362) 0.1382) 0.1582) 0.1372) 0.1461) 0.1391) AP 0.036 0.031 0.042 0.037 0.037 0.033 AR -0.1242) -0.1212) -0.1262) -0.1212) -0.1122) -0.1102) CO AOM 0.1822) 0.1782) 0.1792) 0.2101) 0.2222) 0.2012) AP -0.001 -0.018 -0.028 -0.032 -0.038 -0.027 AR -0.1792) -0.1842) -0.1892) -0.1702) -0.1702) -0.1802) NO2 AOM 0.2092) 0.1822) 0.2232) 0.2262) 0.2452) 0.2162) AP -0.025 -0.052 -0.048 -0.0611) -0.0701) -0.048 AR -0.1572) -0.1692) -0.1802) -0.1432) -0.1262) -0.1512) O3 AOM -0.1131) -0.1202) -0.1712) -0.1322) -0.1242) -0.1172) AP -0.034 -0.047 -0.033 -0.027 -0.049 -0.052 AR 0.008 0.021 0.019 0.035 0.007 0.002 平均温度 AOM -0.2872) -0.2802) -0.2672) -0.2722) -0.2652) -0.2612) AP 0.058 0.0611) 0.0701) 0.0731) 0.0651) 0.0771) AR 0.3932) 0.4032) 0.4062) 0.4172) 0.4112) 0.4132) 平均气压 AOM 0.1132) 0.1042) 0.1002) 0.1322) 0.1402) 0.1302) AP -0.056 -0.0782) -0.0852) -0.100 -0.0771) 0.0761) AR 0.0912) 0.005 -0.0012) 0.000 -0.023 -0.018 平均湿度 AOM 0.007 0.011 -0.020 -0.076 0.003 0.005 AP 0.053 0.0621) 0.047 0.018 0.041 0.015 AR 0.1152) 0.1182) 0.1292) 0.0972) 0.1522) 0.1492) 平均风速 AOM -0.0672) -0.018 -0.056 -0.1201) -0.1132) -0.0711) AP -0.001 -0.002 -0.005 0.022 -0.007 -0.004 AR -0.040 -0.024 -0.031 -0.006 0.1022) -0.029 表 7 环境气象因素对儿童耳鼻喉科相关疾病的累积滞后效应分析
环境因素 疾病 累积滞后1 d 累积滞后2 d 累积滞后3 d 累积滞后4 d 累积滞后5 d 累积滞后6 d AQI AOM 0.2122) 0.2302) 0.2562) 0.2742) 0.2772) 0.2932) AP -0.013 -0.019 -0.015 -0.030 -0.034 -0.034 AR -0.2572) -0.2932) -0.2982) -0.3202) -0.3322) -0.3522) PM2.5 AOM 0.2462) 0.2652) 0.2772) 0.3072) 0.3082) 0.3252) AP 0.017 0.018 0.018 0.003 0.003 0.004 AR -0.2442) -0.2802) -0.2872) -0.3042) -0.3122) -0.3232) PM10 AOM 0.214 0.240 0.253 0.274 0.279 0.290 AP -0.035 -0.044 -0.050 -0.0601) -0.0681) -0.0691) AR -0.2762) -0.3042) -0.3052) -0.3302) -0.3452) -0.3662) SO2 AOM 0.1492) 0.1532) 0.2282) 0.1572) 0.1562) 0.1552) AP 0.030 0.031 0.036 0.034 0.040 0.038 AR -0.1242) -0.1282) -0.1342) -0.1322) -0.1352) -0.1312) CO AOM 0.2122) 0.2272) 0.2602) 0.2422) 0.2432) 0.2552) AP 0.005 -0.009 -0.016 -0.022 -0.021 0.020 AR -0.1892) -0.2072) -0.2272) -0.2262) -0.2412) -0.2412) NO2 AOM 0.2402) 0.2482) 0.2342) 0.2922) 0.2912) 0.3152) AP -0.038 -0.052 -0.0572) -0.0702) -0.0741) -0.0781) AR -0.1672) -0.1892) -0.2112) -0.2192) -0.2312) -0.2362) O3 AOM -0.1212) -0.1252) -0.1282) -0.1362) -0.1351) -0.1392) AP -0.032 -0.039 -0.040 -0.037 -0.040 -0.041 AR -0.006 0.014 0.020 0.024 0.025 0.020 平均温度 AOM -0.2872) -0.2852) -0.2822) -0.2852) -0.2832) -0.2842) AP 0.0651) 0.0651) 0.0671) 0.0691) 0.0711) 0.0721) AR 0.4002) 0.4072) 0.4092) 0.4172) 0.4182) 0.4192) 平均气压 AOM 0.1692) 0.1752) 0.1622) 0.1812) 0.1522) 0.1822) AP -0.0711) -0.0842) -0.1142) -0.1101) -0.1162) -0.1142) AR -0.0912) -0.0962) -0.1092) -0.1372) -0.1372) -0.1592) 平均湿度 AOM -0.003 0.000 -0.033 -0.016 -0.015 -0.014 AP 0.0631) 0.0671) 0.0681) 0.0611) 0.055 0.053 AR 0.1332) 0.1382) 0.1482) 0.1512) 0.1552) 0.1662) 平均风速 AOM -0.1302) -0.1282) -0.1332) -0.1462) -0.1622) -0.1742) AP 0.013 0.019 0.023 0.033 0.031 0.028 AR 0.0621) 0.0771) 0.0832) 0.0952) 0.1152) 0.1152) -
[1] Wang S, Hao J. Air quality management in China: issues, challenges, and options[J]. J Environ Sci(China), 2012, 24(1): 2-13.
[2] 许政敏, 张建基. 儿童急性中耳炎诊疗-临床实践指南(2015年制定)[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志, 2016, 31(2): 15-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSEK201602002.htm
[3] 崔亮亮, 李新伟, 耿兴义, 等. 2013年济南市大气PM25污染及雾霾事件对儿童门诊量影响的时间序列分析[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2015, 32(6): 489-489. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJYJ201506006.htm
[4] 李燕萍, 许洪波, 魏洁, 等. PM2.5和空气质量指数对耳鼻咽喉科急症的影响[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(1): 7-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201801002.htm
[5] 张玲, 黄春江, 王艺, 等. 空气中各污染物浓度与儿童急性中耳炎、急性扁桃体炎发生的相关性[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2019, 33(1): 78-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4706.2019.01.017
[6] 张弛, 吴玮, 顾建文, 等. 大气污染与儿童急性中耳炎、急性扁桃体炎就诊人数的相关性调查[J]. 解放军预防医学杂志, 2017, 35(3): 218-221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYYX201703006.htm
[7] 陆颖霞, 梁洁琼, 谷庆隆, 等. 北京地区儿童AOM发病特点及其与气象因素的相关性研究[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 52(10): 724-728. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2017.10.002
[8] Lin YK, Chang SC, Lin C, et al. Comparing ozone metrics on associations with outpatient visits for respiratory diseases in Taipei Metropolitan area[J]. Environ Pollut, 2013, 177: 177-184. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.12.010
[9] 廖纪萍, 王广发. 大气污染与呼吸系统疾病[J]. 中国医学前沿杂志, 2014, 6(2): 22-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXQY201402010.htm
[10] Wang KY, Chau TT. An association between air pollution and daily outpatient visits for respiratory disease in a heavy industry area[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(10): e75220. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075220
[11] Curtis S, Fair A, Wistow J, et al. Impact of extreme weather events and climate change for health and social care systems[J]. Environ Health, 2017, 16(Suppl 1): 128.
[12] 翟敏. 学龄儿童呼吸系统疾病的环境影响因素研究[J]. 现代预防医学, 2008, 35(19): 3690-3690. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8507.2008.19.004
[13] Hassan MZ, Chowdhury MAB, Hassan I, et al. Respiratory viral infection in early life and development of asthma in childhood: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2019, 98(18): e15419.
[14] 向荣, 许昱, 欧劲. 空气污染对儿童变应性鼻炎影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国医药导报, 2014, 11(15): 109-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY201415037.htm
[15] Kim HH, Lee CS, Jeon JM, et al. Analysis of the association between air pollution and allergic diseases exposure from nearbysources of ambient air pollution within elementary school zones in four Korean cities[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2013, 20(7): 4831-4846. doi: 10.1007/s11356-012-1358-2
[16] 陈洁, 李幼瑾, 江帆, 儿童变应性鼻炎气象环境因素研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2014, 14(28): 1015-1019. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201414002.htm
[17] Wang Y, Zhang YS, Li XP. The effect of air pollution on hospital visits for respiratory symptoms in urban areas of Jinan[J]. China Environ Sci, 2008, 28(6): 571-576.
[18] Teng B, Zhang X, Yi C, et al. The Association between Ambient Air Pollution and Allergic Rhinitis: Further EpidemiologicalEvidence from Changchun, Northeastern China[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2017, 14(3): 226-242. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14030226
-




 下载:
下载: