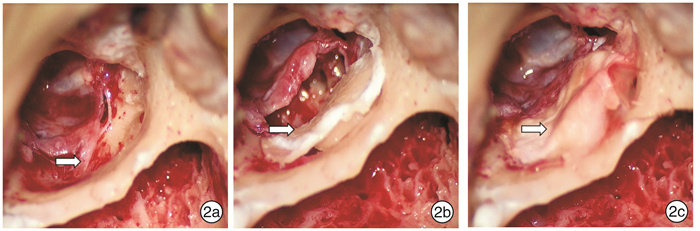
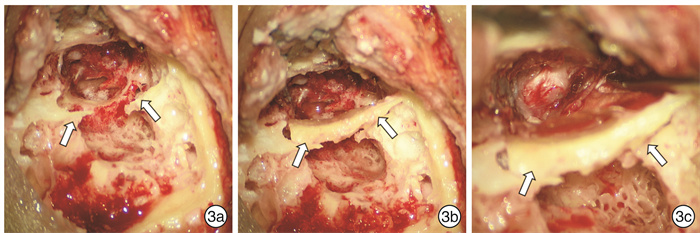
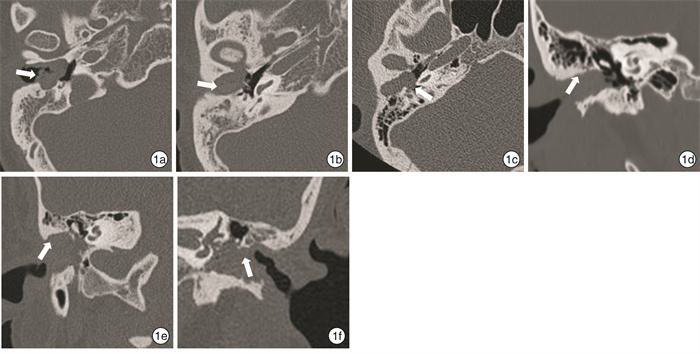
Clinical features and surgical treatment of external auditory canal cholesteatoma in 149 cases
-
摘要: 目的 探讨Ⅰ~Ⅳ型外耳道胆脂瘤(EACC)的临床特征、手术方式及治疗效果。方法 根据EACC分型及术中病变范围对149例(150耳)EACC患者采取不同的手术方式:①44耳采取外耳道病变去除+伴或不伴外耳道成型或外耳道口扩大术; ②23耳采取外耳道病变去除+外耳道成型+鼓室成形术(Ⅰ~Ⅲ型); ③32耳采取外耳道病变去除+外耳道成型+改良乳突根治+外耳道后壁重建术; ④28耳采取外耳道病变去除+外耳道成型+鼓室成形术(Ⅰ~Ⅲ型)+改良乳突根治+外耳道后壁重建术; ⑤12耳采取开放式乳突根治+外耳道成形; ⑥11耳采取上鼓室开放+鼓室成形术+外侧壁重建术。结果 Ⅰ型38耳,Ⅱ型52耳,Ⅲ型58耳,Ⅳ型2耳。所有患者均随访6个月以上,术后均干耳,听力均不同程度提高,复发率低。结论 EACC病变形式多样化,手术方式宜根据乳突气化程度、病变严重程度及听力状况个体化选择。有效的术后随访可减少复发,避免二次手术。Abstract: Objective The aim of this study is to explore the clinical characteristics, surgical management and treatment results of type Ⅰto type Ⅳ external auditory canal cholesteatoma(EACC).Method One hundred and forty-nine patients(150 ears) with EACC underwent different surgical approach according to the classification of EACC and the lesion range: ① 44 ears: external auditory canal lesion resection with or without reconstruction of external auditory canal ② 23 ears: external auditory canal lesion resection with reconstruction of external auditory canal and the tympanoplasty(TypesⅠto Ⅲ); ③ 32 ears: external auditory canal lesion resection with reconstruction of external auditory canal and modified mastoidectomy and reconstruction of the posterior wall of external auditory canal; ④ 28 ears: external auditory canal lesion resection with reconstruction of external auditory canal and tympanoplasty(Types Ⅰ to Ⅲ) and modified mastoidectomy and reconstruction of the posterior wall of external auditory canal; ⑤12 ears: canal wall down mastoidectomy (CWD) with plasty of the cavity of auricular concha; ⑥ 11 ears: epitympanum dectomy and reconstruction with tympanoplasty.Result In the 150 ears, there were 38 ears classified as Type Ⅰ, 52 as Type Ⅱ, 58 as Type Ⅲ and 2 as Type Ⅳ based on the Shin classification. All patients were followed up for more than half a year. The postoperative outcomes were satisfactory with low rate of cholesteatoma recurrence and the hearing was improved to varying degrees.Conclusion Base on the variety of lesions, the surgical treatment method of choice depends on the extent of the lesion. Effective postoperative follow-up can reduce recurrence and avoid the second operation.
-
Key words:
- cholesteatoma /
- external canal /
- therapy /
- surgical management
-

-
[1] Piepergerdes MC, Kramer BM, Behnke EE. Keratosis obturans and external auditory canal cholesteatoma[J]. Laryngoscope, 1980, 90(3): 383-391. doi: 10.1002/lary.5540900303
[2] Sayles M, Kamel HA, Fahmy FF, et al. Operative management of external auditory canal cholesteatoma: case series and literaturereview[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2013, 127(9): 859-866. doi: 10.1017/S0022215113001850
[3] Chawla A, Ezhil Bosco JI, Lim TC, et al. Computed Tomography Features of External Auditory Canal Cholesteatoma: A PictorialReview[J]. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol, 2015, 44(6): 511-516. doi: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2015.05.001
[4] Shin SH, Shim JH, Lee HK. Classification of external auditory canal cholesteatoma by computed tomography[J]. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol, 2010, 3(1): 24-26. doi: 10.3342/ceo.2010.3.1.24
[5] Holt JJ. Ear canal cholesteatoma[J]. Laryngoscope, 1992, 102(6): 608-613. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199206000-00004
[6] Heilbrun ME, Salzman KL, Glastonbury CM, et al. External auditory canal cholesteatoma: clinical and imaging spectrum[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2003, 24(4): 751-756.
[7] Yoon YH, Park CH, Kim EH, et al. Clinical characteristics of external auditory canal cholesteatoma in children[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2008, 139(5): 661-664. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2008.08.028
[8] 周霓, 李玲波, 林琳. Ⅱ-Ⅳ型外耳道胆脂瘤临床特征及手术治疗[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 30(16): 1287-1289, 1296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201616007.htm
[9] 徐帅, 郭洁, 范崇盛. 外耳道胆脂瘤的临床特点与手术方式的选择[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2018, 16(3): 352-355. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2018.03.019
[10] Darr EA, Linstrom CJ. Conservative management of advanced external auditory canal cholesteatoma[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2010, 142(2): 278-280. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2009.10.035
[11] Dähn J, Anschuetz L, Konishi M, et al. Endoscopic Ear Surgery for External Auditory Canal Cholesteatoma[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2017, 38(5): e34-e40. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001386
[12] 尹治军. 显微镜联合耳内镜手术治疗Ⅱ~Ⅲ期外耳道胆脂瘤[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2017, 24(12): 653-654. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT201712016.htm
[13] 顾凤明. 侵及中耳的Ⅲ期外耳道胆脂瘤的手术方法探讨[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2017, 23(3): 275-276, 279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZEBY201703019.htm
[14] Kim CW, Baek SH, Lee SH, et al. Clinical characteristics of spontaneous cholesteatoma of the external auditory canal in children comparing with cholesteatoma in adults[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2014, 271(12): 3179-3185. doi: 10.1007/s00405-013-2820-6
[15] 宋忠义, 于学民, 王春芳, 等. 累及鼓室和乳突的外耳道胆脂瘤的手术治疗[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(12): 937-940. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201812014.htm
[16] Ho KY, Huang TY, Tsai SM, et al. Surgical Treatment of External Auditory Canal Cholesteatoma-Ten Years of Clinical Experience[J]. J Int Adv Otol, 2017, 13(1): 9-13. doi: 10.5152/iao.2017.2342
[17] Naim R, Linthicum F Jr, Shen T, et al. Classification of the external auditory canal cholesteatoma[J]. Laryngoscope, 2005, 115(3): 455-460. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000157847.70907.42
[18] Konishi M, Iwai H, Tomoda K. Reexamination of Etiology and Surgical Outcome in Patient With Advanced External Auditory Canal Cholesteatoma[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2016, 37(6): 728-734. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001079
[19] Vrabec JT, Chaljub G. External canal cholesteatoma[J]. Am J Otol, 2000, 21(5): 608-614.
[20] Ursick JA, Brackmann DE. External auditory canal cholesteatoma[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2012, 91(7): 270-270. doi: 10.1177/014556131209100702
[21] Shinnabe A, Hara M, Hasegawa M, et al. A comparison of patterns of disease extension in keratosis obturans and external auditorycanal cholesteatoma[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2013, 34(1): 91-94. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e318277a5c8
-




 下载:
下载: